
Ever been at the bar, beer in hand, hearing tales of a magic pill that turns a regular guy into a laser-focused dynamo? That’s Adderall for you. Maybe your gym buddy swears by it, or you’ve popped one before a grueling work session. It’s everywhere, man. But the burning question remains: how does Adderall work? Beyond the locker room chatter and bro-science, what’s the real deal with this prescription drug? Let’s cut through the noise, break down the science, and get to the core of how Adderall truly revs up the central nervous system. Buckle up, gents—it’s going to be an enlightening ride.
What Exacly is Adderall?
History of Adderall: From Trenches to Tablets
Alright, fellas, let’s take a trip down memory lane. Before Adderall was the go-to prescription stimulant for that college all-nighter or the 9-to-5 grind, its main component, amphetamine, was the stuff of legends.
Amphetamine’s Grand Entrance: Picture this: the 1800s. A Romanian genius named Lazar Edeleanu cooks up amphetamine for the first time in 1887. Fast forward a few decades, and by the 1930s, “Benzedrine” or the slick “Bennies” was the talk of the town.
Soldiers’ Secret Sauce: Jump to World War II. Those brave lads hitting the beaches and holding the lines. They had a trick up their sleeves: pep pills. Pure, uncut amphetamine. And it wasn’t just our boys; even the Axis were popping them. Rumor has it, Hitler himself was on the amphetamine train, taking shots of it on the daily! By the time peace treaties were signed, a staggering 150 million pills had been handed out. And the love for amphetamine didn’t stop with WWII; it was the wingman for soldiers in Korea and Vietnam.
The Evolution of Adderall: After the wars, amphetamine was the wild child of the civilian world. But here’s the deal: pure amphetamine was like a sledgehammer—powerful but not always precise. There was a need for something more controlled, more refined. Enter Roger Griggs and James Parker, two pharma bros who took this challenge head-on. They tweaked the OG amphetamine recipe to aim to treat ADHD without the overkill. By ’96, Adderall rolled out, a smoother blend of dextroamphetamine and levoamphetamine. It was the refined answer to the raw power of pure amphetamine.
Adderall’s Chemical Blueprint: Unraveling the Amphetamine Salts
Adderall stands out in the pharmaceutical world due to its unique composition of two primary amphetamine salts: dextroamphetamine and levoamphetamine. But to truly grasp their significance, we need to dissect their chemical characteristics.

Dextroamphetamine: Often referred to as the right-handed (or “dextrorotatory”) form of amphetamine, this molecule has a specific spatial arrangement. In the vast realm of organic chemistry, even a slight twist or turn in a molecule’s structure can drastically alter its effects. Dextroamphetamine is known for its potent stimulatory action on the central nervous system, making it a key player in the stimulant arena.
Levoamphetamine: This is the left-handed (or “levorotatory”) twin of dextroamphetamine. While it might seem like a mere mirror image on paper, in the biological world, this distinction is paramount. Levoamphetamine tends to be slightly less potent than its dextrorotatory counterpart but brings a more prolonged, sustained stimulatory effect to the table.
When combined, these two amphetamine salts create a symphony of stimulatory effects. Imagine two musicians, each skilled in their instrument, coming together to produce a harmonious tune. That’s what dextroamphetamine and levoamphetamine achieve in Adderall. Their combined effects result in a well-rounded stimulant experience, balancing immediate potency with lasting impact.
In essence, Adderall’s chemical makeup is a meticulously crafted blend of these amphetamine salts, each contributing its distinct characteristics to produce the final therapeutic effect.
How Adderall Grooves in Your Brain
Picture a bustling club, lights flashing, and the energy palpable. In one corner, there’s Dopamine, looking sharp but a tad reserved. He’s got the moves, the rhythm, but there’s a hitch. Sometimes, especially in those with ADHD, Dopamine gets easily distracted or feels too shy. He’s been eyeing that stunning girl on the dance floor, “The Dopamine Receptor”, but can’t muster the courage to approach her.
“Is my cologne too strong? Wait, did I even wear cologne? Is my hair looking okay? Oh man, I hope my breath is fresh. And why do all the bartenders have blond hair? Is there a secret club policy to hire only blondes?” The distractions are endless, and the dance floor seems miles away.
Enter Adderall, dropping Usher’s “DJ Got Us Fallin’ in Love” on the sound system. The beat is infectious, and the lyrics are compelling. It’s as if the song speaks directly to Dopamine: Adderall, acting like this iconic track, gives Dopamine that much-needed nudge, a boost of confidence. It amplifies his natural rhythm, fine-tuning his focus and making him feel like he’s “on top of the world tonight.”
With the music guiding him and Adderall’s influence, Dopamine finds himself moving toward the dopamine Receptor. And as the chorus hits, “Cause baby tonight, the DJ got us falling in love again,” they lock eyes. The chemistry is undeniable. Dopamine, now supercharged, takes the lead, and they begin to dance in perfect harmony, representing the enhanced neurotransmitter-receptor interaction in the brain.
But it’s not just the music or Adderall’s push. The entire club, representing the neural pathways, erupts in cheer. Neurotransmitters, acting like Dopamine’s buddies, cheer him on, ecstatic that he’s finally dancing with Receptor. They’re the friends who’ve been waiting for this moment, thrilled to see Dopamine finally “get that girl.”
This dance, this connection, is a beautiful representation of how Adderall optimizes brain function. It ensures that Dopamine, often shy or distracted in those with ADHD, finds its perfect match in Receptor, facilitating better focus, mood, and overall cognitive function.
So in short, lack of attention and focus, especially in those with ADHD, can be likened to dopamine being hesitant or distracted from interacting with its receptors. Adderall acts as a facilitator or ‘matchmaker,’ encouraging this interaction, which in turn enhances focus.
What is ADHD?
Alright, folks, let’s dive into the world of ADHD. Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) isn’t just some fancy term thrown around; it’s a legit, hard-hitting neurobehavioral disorder. We’re talking about a relentless combo of hyperactivity, impulsivity, and, yeah, sometimes a bit of a struggle to keep the focus locked in.
Now, if you think this is some rare, once-in-a-blue-moon kind of thing, think again. ADHD is like that popular guy at the party – it’s everywhere, especially in kids. But here’s the kicker: it doesn’t just pack its bags and leave once you hit adulthood. Nope, it sticks around, with about 3.5% to 4.5% of adults still wrestling with it.
And man, the challenges these warriors face? It’s not just about occasionally losing their car keys or forgetting a name. We’re talking real-deal struggles: tanking grades, risky driving stunts, rocky relationships with pals, and sometimes even crossing paths with the law. And if left unchecked? ADHD can open the door to some heavy hitters like depression, anxiety, and substance abuse1.
So next time you hear ADHD, know it’s not just some buzzword. It’s a real, gritty journey that many are navigating every single day.
ADHD and Dopamine: More Than Just a “Lack”
So, you’ve probably stumbled upon articles claiming ADHD is all about a lack of dopamine in the brain, right? But let’s cut through the noise and get to the real deal. What does that even mean?
First off, it’s not just about having low dopamine levels. Sure, some research does suggest that folks with ADHD might be running a bit low on this crucial neurotransmitter, which plays a big role in motivation, pleasure, and attention. But that’s just one piece of the puzzle.
The real kicker? It’s not just about how much dopamine you’ve got; it’s about how it’s used to treat you. Some studies have shown that our ADHD brethren might have fewer dopamine receptors, or maybe their receptors are just playing hard to get. This means that even if there’s a decent amount of dopamine cruising around, it’s not always locking in and doing its job effectively. As I described it the analogy in the beginning, sometimes dopamine can be that shy or super distracted guy on the dance floor and the dopamine receptor is running around playing hard to get.
And then there’s the reuptake game. Imagine dopamine as a car on a highway. In some ADHD brains, it’s like these cars are getting pulled off the road too quickly, not reaching their destination. Stopping to take pictures or getting pulled over or whatever. This rapid removal from the scene, before dopamine can make its mark, can contribute to those classic ADHD symptoms.
Bottom line? ADHD’s relationship with dopamine isn’t just a simple numbers game. It’s a complex dance of levels, receptor interactions, and timing. So next time someone oversimplifies it as just a “dopamine deficiency,” you’ll know there’s a whole lot more to the story.
Adderall’s Impact: ADHD vs. The Average Brain
Alright, guys, let’s break it down. If you’ve got ADHD, your brain’s like a high-performance car with a slight hiccup in the ignition. You’ve got the horsepower, but sometimes it’s hard to get the engine purring just right. That’s where Adderall steps in, like a top-tier mechanic fine-tuning that engine.
Now, for someone with ADHD, everyday tasks can feel like trying to watch a movie with someone constantly changing the channel. Imagine you’re deep into a gripping scene, and suddenly you’re watching a cooking show, then a wildlife documentary, and then back to the movie, but you’ve missed the crucial parts. Frustrating, right? That’s a day in the life of someone with ADHD.
Enter Adderall. This bad boy acts like a remote lock, helping you stay on your chosen channel. It boosts the activity of dopamine and norepinephrine in the brain, making you feel more dialed in and less like you’re bouncing off the walls.
But here’s the kicker: there’s chatter out there, especially among college folks, thinking Adderall’s like some brain-boosting magic pill, even if you don’t have ADHD. But let’s set the record straight. A deep dive into the US National Library of Medicine tells us that while Adderall does wonders for those with ADHD, its cognitive-enhancing effects on the average Joe aren’t as clear-cut as some might think. So, before you buy into the hype, get the facts straight.
In a recent publication from the Pharmacy journal, some intriguing findings about Adderall were presented. The research indicates that while a standard 30 milligram dose can indeed enhance attention and focus, it doesn’t necessarily elevate performance in areas like short-term memory, reading comprehension, and fluency.
Lisa Weyandt, the lead researcher, provided clarity on the matter: “For those whose brains are already functioning optimally in these domains, the medication might not offer a cognitive advantage. In fact, it could even be counterproductive. Essentially, Adderall is designed to normalize focus for those who are inherently unfocused, rather than supercharge an already efficient system.”
The Paradoxical Calm of Adderall in ADHD
Ever bumped into someone with ADHD who’s practically bouncing off the walls, but the moment they pop an Adderall, they’re as serene as a monk in meditation? Sounds backward, right? Welcome to the world of the Paradoxical Effect.
Here’s the deal: Adderall, as we’ve touched on, boosts dopamine release. Now, for most folks, this surge in dopamine translates to increased alertness and focus. But for some, especially those hyperactive souls, it’s like pouring water on a fire. The heightened dopamine levels bring their overactive brain circuits down a notch, leading to a calm they rarely experience.
Picture it like this: Imagine a car engine revving non-stop, burning fuel like there’s no tomorrow. Now, instead of pushing the gas pedal further, you pour in a stabilizer. The engine starts to purr smoothly, no longer in overdrive. That’s the Paradoxical Effect in action.
For the science buffs, this isn’t just anecdotal. Research has delved into this phenomenon, highlighting the brain’s intricate dance with neurotransmitters and how individual differences play a massive role.
Remember, the brain’s a complex beast. What soothes one person might rev up another. It’s all about understanding the unique wiring and finding the right balance.
Adderall XR vs. Regular Adderall: The Showdown
Navigating the world of ADHD medications can feel like deciphering a complex puzzle. Two heavyweights in this arena are Adderall and its extended counterpart, Adderall XR. Let’s break down the match-up:
Regular Adderall:
Quick Fix: This guy gets to work fast, giving you that immediate ADHD symptom relief.
Staying Power: Think of it like a morning coffee – it
gives you a boost, but by theafternoon, you might need another shot. Lasts about 4-6 hours.
Dose Routine: You’ll likely pop it a couple of times a day to keep things steady.
Ideal For: Those days when you need a quick pick-me-up or want to adjust doses based on what’s on your plate.
Adderall XR:
Smooth Operator: It kicks off strong, releasing half its mojo right away, then cruises steadily, dishing out the rest over time.
Endurance: This one’s your marathon runner, covering you for a solid 10-12 hours.
One and Done: Pop one in the morning, and you’re set for the day.
Perfect For: Folks who want that all-day coverage without the mid-day med reminders.
So, in the grand scheme of ADHD meds, both these players have their game. Regular Adderall’s got that flexibility, while XR’s all about the long game.
Adderall vs. Meth: A Close Look at Two Very Different Substances
You might’ve heard whispers comparing Adderall to methamphetamine, commonly known as meth. On the surface, it might seem like an outrageous comparison, but when you dive into the chemistry, there are indeed similarities. However, it’s crucial to understand that while they share structural similarities, their effects, uses, and dangers are worlds apart.
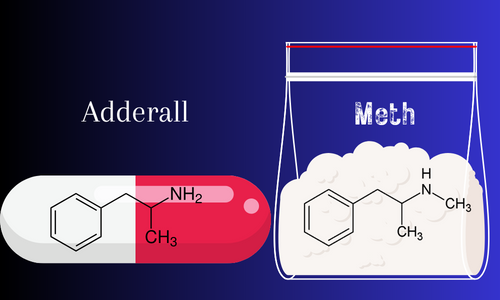
Chemical Cousins, But Not Twins
At a molecular level, Adderall and methamphetamine do share a structural backbone. Think of them like two houses built with similar blueprints but with vastly different interiors and purposes.
To give you a non-chemical analogy: imagine you have two cups of coffee. One is your standard morning brew, and the other has a shot of moonshine. While both cups contain coffee, that added component in the second cup transforms it into something entirely different, with a distinct purpose and effect.
Similarly, the addition or modification of certain groups in the molecular structure can drastically change a compound’s properties. Methamphetamine has an additional methyl group compared to the amphetamine salts in Adderall. This might sound minor, but in the world of chemistry, such a change can significantly alter how a substance interacts with the body.
Effects on Dopamine and Its Receptors
Both Adderall and methamphetamine influence dopamine, but the intensity and consequences of their interactions are distinct.
Adderall: As we’ve discussed, Adderall primarily works by increasing the activity of dopamine and norepinephrine in the brain. It helps dopamine stay in the synapses longer, allowing for enhanced neurotransmitter-receptor interaction. This results in improved focus and reduced impulsivity, especially in individuals with ADHD.
Methamphetamine: Meth takes things to an extreme. It floods the brain with dopamine, leading to intense euphoria. But here’s the catch: this flood is more like a tsunami, overwhelming the brain’s dopamine system. Over time, this can damage the dopamine receptors, making it harder and harder for the brain to experience pleasure without the drug. This leads to increased dependency and a host of other health issues.
The Bottom Line
While Adderall and methamphetamine might be distant chemical cousins, they’re used and regulated very differently for good reasons. Adderall, when prescribed and taken correctly, can be beneficial for those with ADHD. Methamphetamine, on the other hand, is a potent and illegal drug with a high potential for abuse and severe health consequences.
Always remember: just because two things share similarities doesn’t mean they’re the same. A rose by any other name might smell as sweet, but when it comes to chemicals, a slight tweak can make all the difference in the world.
Non-Stimulant Prescription Drugs for ADHD
Discover the comprehensive guide to non-stimulant prescription drugs for ADHD on our blog. As ADHD treatments continue to evolve, it’s essential to understand the benefits and mechanisms of non-stimulant options. Dive deep into the latest research, patient testimonials, and expert insights, offering a well-rounded perspective for those seeking alternatives to traditional stimulant medications. Learn more about how these treatments can effectively manage ADHD symptoms without the typical side effects of stimulants. CLICK HERE FOR FULL ARTICLE!
Nootropics: Adderall Alternatives Worth Exploring
While Adderall is a leading ADHD medication, the nootropic world offers non-prescription alternatives that can enhance cognition:
1. Mucuna Pruriens & L-Tyrosine: Dopamine Boosters
Mucuna Pruriens (Velvet Bean): A source of L-DOPA, it aids in dopamine production, offering mood, motivation, and focus benefits.
L-Tyrosine: An amino acid that supports dopamine production by converting to L-DOPA.
Comparison: Unlike Adderall’s direct dopamine release, these provide the brain with the necessary components for natural dopamine production.
2. Bacopa Monnieri & Rhodiola Rosea: Herbal Enhancers
Bacopa Monnieri: An Ayurvedic herb that improves synaptic communication, enhancing memory and cognitive processing over time.
Rhodiola Rosea: An adaptogen that combats fatigue and boosts energy and focus.
Comparison: While Adderall offers an immediate boost, these herbs promote long-term brain health and function.
3. Pramiracetam & Phenylpiracetam: Racetam Powerhouses
Pramiracetam: Focuses on boosting acetylcholine, enhancing memory and learning without a stimulant effect.
Phenylpiracetam: A balanced racetam that enhances cognition and offers mild stimulation due to its dopamine interaction.
Comparison: Adderall provides strong alertness, while racetams offer cognitive enhancement with varying degrees of stimulation.
In essence, while Adderall provides a direct stimulant effect, these nootropics offer a range of cognitive benefits, each with its unique mechanism of action.
Side Effects and Risks of Adderall
Alright, bros, let’s keep it 100. Every superhero has its kryptonite and Adderall’s no exception. While it’s been a game-changer for many, especially those battling ADHD symptoms, it’s essential to be in the know about the potential hiccups. Knowledge is your armor, so let’s gear up and dive into the research.
Adderall Risks and Side Effects: A Comprehensive Overview
Adderall, a potent stimulant medication primarily prescribed to treat ADHD, has garnered significant attention due to its potential risks and side effects. While it can be a game-changer for many with ADHD, it’s crucial to understand the full spectrum effects of adderall and its impact on the body and mind.
1. Cardiovascular Concerns: High doses of Adderall can lead to increased blood pressure and heart rate. There’s an elevated risk of sudden death, especially in those with pre-existing heart conditions. Moreover, the FDA has highlighted concerns regarding the drug’s potential to cause heart-related problems, especially in adults source.
2. Neurological Impacts: Adderall works by altering brain chemistry, specifically increasing norepinephrine and dopamine levels. This can lead to mood swings, panic attacks, and even severe psychological reactions in some individuals.
3. Physical Dependence and Withdrawal: Habit-forming when misused, Adderall can lead to substance use disorder. Withdrawal symptoms can be intense, including fatigue, depression, and intense cravings. Over time, misuse drug abuse can also lead to a physical dependence on the drug.
4. Interactions with Other Medications: It’s essential to be wary of drug interactions prescribed adderall, especially with MAO inhibitors, as they can lead to adverse effects. Always consult with a healthcare professional before combining Adderall with other medications.
5. Potential for Misuse: Often dubbed the “study drug,” Adderall’s misuse, especially in higher doses, can lead to severe health risks, including addiction. Those without ADHD might misuse it to improve focus or lose weight, but this comes with significant dangers.
6. Side Effects Spectrum: Common side effects include difficulty breathing, allergic reactions, and daytime sleepiness. Some might experience adverse effects like mood swings, stress hormone fluctuations, and even false test results in specific scenarios.
7. Impact on Growth: There’s a concern, especially among pediatric professionals, about Adderall’s potential to stunt a child’s growth. The exact mechanisms remain under study, but it’s a point of consideration for long-term use in younger patients.
8. Sleep and Mood Disorders: Adderall can exacerbate sleep disorders due to its stimulant nature. Additionally, it might lead to mood disorders, including bipolar disorder, especially in those predisposed to such conditions.
The Verdict: To Pop or Not to Pop?
Alright, gents, we’ve taken a deep dive into the world of Adderall, from its historical roots to its intricate dance with our brain’s neurotransmitters. But the million-dollar question remains: is Adderall right for you?
If you’re battling ADHD, this drug might be your knight in shining armor, helping you navigate the daily challenges and bringing a semblance of order to the chaos. But remember, every individual is unique. What works wonders for one might not be the best fit for another. It’s essential to consult with a medical professional, weigh the pros and cons, and make an informed decision.
For those without ADHD, tread with caution. While the allure of heightened focus and energy might be tempting, especially in today’s fast-paced world, the risks associated with misuse are real. It’s not just about the potential for addiction; it’s about the broader impact on your mental and physical health.
Final Thoughts:
Adderall, like any drug, is a tool. Used correctly, under the guidance of a healthcare professional, it can be transformative. But like any tool, it can cause harm if misused. Stay informed, prioritize your well-being, and always approach any medication with a healthy dose of respect and caution.
Remember, gents, knowledge is power. Equip yourself with the facts, make informed decisions, and always prioritize your health and well-being.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this blog is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Always consult with a healthcare professional before making any decisions related to medication or treatment.
FAQ’s
Q: What are the potential drug interactions when taking Adderall with over-the-counter medications?
A: Taking Adderall alongside certain over-the-counter (OTC) medications can lead to adverse effects. For instance, combining Adderall with cold or allergy medicines that contain decongestants can increase heart rate and high blood pressure. Always consult with a healthcare professional before mixing Adderall with any OTC drugs.
Q: How does Adderall affect people with bipolar disorder or mood swings?
A: Adderall can exacerbate mood swings, especially in individuals with bipolar disorder. The stimulant nature of the drug can potentially trigger manic episodes. It’s crucial for individuals with bipolar disorder to discuss potential risks with their healthcare provider before starting Adderall.
Q: Is it safe to use Adderall as a study drug or for weight loss in individuals without ADHD?
A: Using Adderall as a “study drug” or for weight loss is not FDA-approved and can be dangerous. Misuse can lead to increased health risks, including substance use disorder, heart issues, and severe psychological effects. It’s essential to use Adderall only as prescribed and for its approved medical reasons.
Q: How does the immediate release version of Adderall differ from other versions?
A: The immediate release (IR) version of Adderall provides rapid symptom relief but lasts only about 4-6 hours. In contrast, Adderall XR, an extended-release version, offers a more prolonged effect, lasting 10-12 hours. The choice between them depends on individual needs and a physician’s recommendation.
Q: Are there non-stimulant medications available for treating ADHD?
A: Yes, there are non-stimulant medications available for treating ADHD. These drugs work differently than stimulants like Adderall and might be a suitable option for those who don’t respond well to stimulant medications or experience adverse effects from non-stimulant medication. Always consult with a healthcare provider to explore the best treatment options.
Q: How does Adderall use affect norepinephrine levels in the brain?
A: Adderall increases the levels of both dopamine and norepinephrine in the brain. Norepinephrine plays a crucial role in attention and response actions. By boosting its levels, Adderall helps improve attention span, focus, and reduces impulsivity in individuals with ADHD.
Q: What are the risks of taking higher doses of Adderall than prescribed?
A: Taking higher doses of Adderall than prescribed can lead to severe health complications, including increased blood pressure, heart problems, and a higher risk of substance use disorder. Overdosing can also lead to panic attacks, difficulty breathing, and in extreme cases, sudden death. It’s imperative to take Adderall only as directed by a medical professional.
References:
Chemical structure and effects of amphetamine salts
US National Library of Medicine
“6 Things to Know About Adderall.” Lee Health. Link
Sumners, Christina. “You Asked: What does Adderall do to your body?” Vital Record, Texas A&M Health Science Center, September 22, 2015. Link
“ADDERALL (CII).” U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Link
